
Blockchain in the Maritime Community – 2
As we continue our exploration of blockchain’s transformative potential in the maritime maintenance sector, it’s clear that this technology holds the promise of significant advancements. In the first part of our discussion, we delved into the fundamental principles of blockchain technology and how it can enhance supply chain management and asset tracking in the maritime industry. We saw how blockchain’s transparency, immutability, and decentralisation can improve traceability, accountability, and efficiency in these areas.
Now, as we move forward, we will delve deeper into additional use-cases of blockchain in maritime maintenance. We will explore how smart contracts can revolutionise maintenance agreements by automating contractual obligations. We will also discuss the role of blockchain in facilitating seamless data sharing and collaboration among the diverse actors involved in maritime maintenance. Let’s continue our journey into the vast potential of blockchain technology in the maritime sector.
Table of Contents
Use-Case 3: Smart Contracts for Maintenance Agreements
Maritime maintenance agreements often involve complex and multilateral arrangements, leading to inefficiencies and disputes. Blockchain-based smart contracts offer a promising solution to streamline these processes by enabling automated and transparent transactions.
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. They are stored on the blockchain, making them transparent, traceable, and irreversible. In the context of maritime maintenance, smart contracts can automate many aspects of the process, including the scheduling of maintenance, confirmation of completion, and even payment.
For example, a smart contract could be set up to automatically schedule maintenance when a ship’s engine reaches a certain usage threshold. Once the maintenance is completed and verified, the smart contract could release payment to the service provider without any manual intervention. This not only streamlines operations but also reduces the chances of disputes and non-payment issues.
Benefits of Smart Contracts in Maritime Maintenance:
- Self-Executing Contracts: Smart contracts execute themselves based on predefined conditions, eliminating the need for third-party intermediaries and reducing time and costs.
- Automated Payments: By linking contractual obligations with payment terms, smart contracts can automatically trigger payments upon the fulfilment of agreed-upon conditions, reducing payment delays and disputes.
- Increased Transparency: Since smart contracts are stored on a blockchain, all parties have access to the same information, ensuring transparency and reducing the potential for miscommunication or manipulation.
Several maritime industry projects are leveraging the power of smart contracts for maintenance agreements. For instance, the Port of Rotterdam’s blockchain project, BlockLab, is exploring the use of smart contracts for various use cases, including equipment leasing and maintenance. By automating contractual obligations and payments, they aim to increase efficiency and reduce disputes in the port’s operations.
Another promising project is VesselBot, a digital chartering platform that uses smart contracts to automate numerous processes involved in chartering, including vessel performance tracking and payment settlements.
These applications demonstrate the significant potential of blockchain-based smart contracts to transform the management of maintenance agreements in the maritime industry. In the next section, we’ll delve into the role of blockchain in data sharing and collaboration within the maritime maintenance sector.
Use-Case 4: Data Sharing and Collaboration
Accurate and timely data sharing among various stakeholders is crucial for operational efficiency in maritime maintenance. However, traditional methods of data exchange often face issues of trust, data silos, and privacy concerns. Blockchain technology offers a unique solution to these challenges, enabling secure, efficient, and transparent data sharing and collaboration.
Blockchain’s decentralised nature and cryptographic security make it an ideal platform for data sharing among various parties involved in maritime maintenance. From ship operators and maintenance service providers to part manufacturers and regulatory bodies, everyone can access and contribute to the data on a need-to-know basis.
Each data entry on the blockchain is time-stamped, transparent, and immutable, ensuring the accuracy and veracity of the information. This facilitates trust among stakeholders, as they no longer have to rely on a central authority to manage and validate the data.
Benefits of Blockchain in Data Sharing and Collaboration:
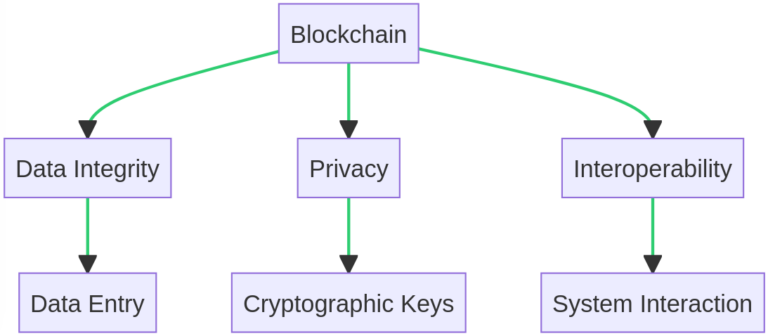
- Data Integrity: Once a data entry is added to the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted. This ensures the integrity of the data and builds trust among stakeholders.
- Privacy: While the blockchain is transparent, it also uses cryptographic techniques to protect sensitive information. Only parties with the right cryptographic keys can access the data, ensuring privacy and compliance with data protection regulations.
- Interoperability: Blockchain provides a common platform where different systems can interact with each other. This facilitates the sharing of data across different systems and processes, breaking down data silos and enhancing collaboration.
Several initiatives are using blockchain to enhance data sharing and collaboration in maritime maintenance. For instance, the Blockchain in Transport Alliance (BiTA) aims to develop blockchain standards and provide educational resources to help the transport industry understand and implement blockchain.
Another example is the Global Shipping Business Network (GSBN), an open digital platform based on distributed ledger technology. GSBN facilitates seamless and efficient data exchange between all stakeholders in the shipping industry, including carriers, terminal operators, customs agencies, and logistics providers.
These use-cases demonstrate that blockchain technology can revolutionise data sharing and collaboration in maritime maintenance, breaking down data silos, enhancing efficiency, and building trust among stakeholders. In the next section, we’ll discuss some of the challenges and considerations to bear in mind when implementing blockchain in this context.
Challenges and Considerations
While blockchain technology offers significant advantages for maritime maintenance, it’s not without its challenges and considerations. Implementing blockchain requires thoughtful planning and a clear understanding of its potential hurdles. This section will delve into some of these challenges and explore ongoing efforts to navigate them.
Adopting blockchain in maritime maintenance involves technological, regulatory, and operational considerations. For instance, organisations will need to decide on the type of blockchain – public, private, or consortium – that best suits their needs. They must also consider factors such as data privacy, user rights, and compliance with international maritime laws and standards.
Additionally, blockchain’s inherent complexity can be a barrier. Teams will need training to understand and manage blockchain systems, and stakeholders may require education to understand the value and use of such systems.
Key Challenges:
- Scalability: As blockchain networks grow, so do the demands on storage, computational power, and network capacity. This can slow down transaction times and increase costs, posing scalability challenges.
- Regulatory Frameworks: The decentralised nature of blockchain can make it difficult to fit within traditional regulatory frameworks. For example, it can be unclear which jurisdiction’s laws apply to a blockchain transaction, especially when it involves multiple countries.
- Interoperability: While blockchain can help break down data silos, it can also create new ones if different blockchains can’t communicate with each other. Ensuring interoperability among various blockchain systems is a significant challenge.
Many efforts are underway to address these challenges. For scalability, solutions like sharding (dividing the blockchain into smaller pieces), off-chain transactions, and layer-two protocols are being explored.
To navigate regulatory issues, some companies are working closely with regulators to shape new laws and guidelines that can accommodate blockchain’s unique properties. Initiatives such as the International Association for Trusted Blockchain Applications (INATBA) are engaging policymakers to promote a global framework for blockchain governance.
Concerning interoperability, initiatives like the Interledger Protocol and Blockchain Interoperability Alliance are working to create standards that enable communication between different blockchain systems.
While the road to blockchain adoption in maritime maintenance may have some hurdles, the potential benefits make the journey worth it. As we’ll discuss in the concluding section, the ability of blockchain to enhance transparency, efficiency, and collaboration holds great promise for transforming maritime maintenance operations.
Conclusion
As we chart our course through the expansive waters of maritime maintenance, it’s evident that blockchain technology brings a transformative potential that’s hard to ignore. Despite the challenges it presents, the diverse use-cases and benefits it offers make it a compelling solution to many of the industry’s longstanding issues.
In this article, we’ve journeyed through several use-cases of blockchain in maritime maintenance, from enhancing supply chain management and asset tracking to streamlining maintenance agreements and facilitating data sharing. The benefits of blockchain, such as transparency, authenticity verification, efficiency improvement, and secure collaboration, have echoed across all these applications.
The strength of blockchain lies in its capacity to foster trust among stakeholders, automate processes, and guarantee the integrity and authenticity of information. By digitising and decentralising maritime maintenance operations, blockchain has the potential to revolutionise practices, making them more transparent, efficient, and resilient.
While we’ve only skimmed the surface of blockchain’s potential, the maritime industry has already begun to recognise its value. Numerous pilot projects and initiatives worldwide are pushing the boundaries of what’s feasible with blockchain in maritime maintenance.
However, this is just the beginning of the journey. As the technology matures and the industry becomes more acquainted with its benefits and use-cases, we anticipate an increasing number of maritime companies will explore and adopt blockchain solutions.
The transformative potential of blockchain technology is vast, and its wave is set to bring a sea of change in maritime maintenance operations. The future is promising, and the industry must be prepared to sail with this wave of innovation.





Leave a Reply